ITIL 4 OVERVIEW
…ITIL 4 – akcelerator za Vaše avanture u svemiru upravljanja uslugama!
“Ako se sve čini pod kontrolom, ne idete dovoljno brzo.” – Mario Andretti

ITIL 4 POSTER
…ITIL 4 – akceleraror za Vaše avanture u svemiru upravljanja uslugama!

UPRAVLJANJE USLUGAMA & ITIL
Usluge su glavni način na koji organizacije stvaraju vrijednost. Danas je većina usluga omogućena informatičkim tehnologijama, a upravljanje IT uslugama (eng. IT Service Management (ITSM)) smatra se ključnom strateškom sposobnošću!

UPRAVLJANJE USLUGAMA
Upravljanje uslugama ( eng. Service Management) je skup specijaliziranih organizacijskih sposobnosti za omogućavanje vrijednosti klijentu u obliku usluga.

ITIL
ITIL je zbirka preporuka najbolje prakse za upravljanje uslugama i globalno najkorišteniji okvir za upravljanje uslugama.

ZAŠTO ITIL 4?
Upravljanje uslugama (eng. Service management) evoluira, a tako i ITIL…
ITIL 4 (2019.) osigurava sustav za učinkovito vladanje i upravljanje IT omogućenim uslugama. ITIL 4 mijenja uspostavljene IT Service Management (ITSM) prakse u širem kontekstu korisničkog iskustva (eng. Customer experience), tokova vrijednosti ( eng. Value streams) i digitalne transformacije, a ujedno prihvaća i nove načine rada, kao što su Lean, Agile i DevOps.
ITIL 4 pruža smjernice organizacijama koje trebaju ovladati novim izazovima upravljanja uslugama i iskoristiti potencijal suvremene tehnologije.

KLJUČNI ITIL 4 KONCEPTI SU…
4 DIMENZIJE UPRAVLJANJA USLUGAMA
( eng. 4 Dimensions of service management)
SUSTAV VRIJEDNOSTI USLUGE
(eng. Service value system (SVS))

4 DIMENZIJE UPRAVLJANJA USLUGAMA
(eng. 4 DIMENSIONS OF SERVICE MANAGEMENT)
… predstavljaju relevantne perspektive upravljanja uslugama koje bi trebalo uzeti u obzir u svemu što radite!
4 DIMENZIJE UPRAVLJANJA USLUGAMA
ITIL 4 naglašava četiri dimenzije koje osiguravanju holistički pristup upravljanju uslugama:
1. Organizacija i ljudi (eng. Organisations & People)
2. Informacije i tehnologija (eng. Information & Technology)
3. Partneri i Podizvođači (eng. Partners & Suppliers)
4. Tokovi vrijednosti i Procesi ( eng. Value Streams & Processes)
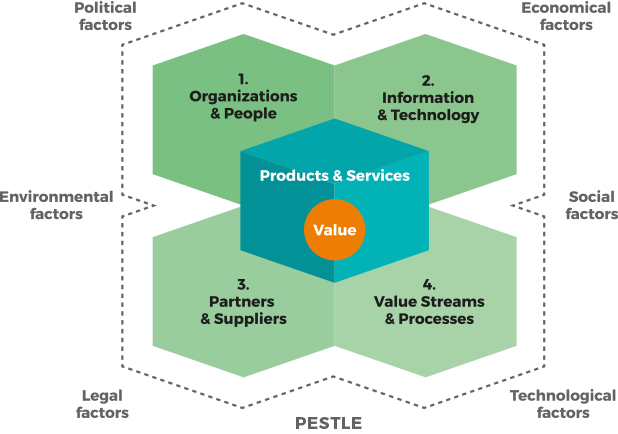
Dajući svakoj od četiri dimenzije odgovarajuću količinu pažnje, organizacija osigurava da njezin sustav vrijednosti usluga (SVS) ostane uravnotežen i učinkovit.

ZAŠTO TOKOVI VRIJEDNOSTI (eng. VALUE STREAMS)?
ITIL 2 and ITIL 3 su nenamjerno stvarali “procesne silose”.
ITIL4 uvodi tokove vrijednosti kako bi poboljšao koordinaciju i integraciju aktivnosti, kao i fokus na stvaranju vrijednosti. Prepoznavanje i razumijevanje različitih tokova vrijednosti koje organizacija ima je presudno za poboljšanje njezinog ukupnog učinka.

TOK VRIJEDNOSTI
(eng. Value stream)
Tok vrijednosti je niz koraka koje organizacija poduzima kako bi stvorila i isporučila potrošačima proizvode i usluge. Tok vrijednosti kombinacija je aktivnosti lanca vrijednosti organizacije. Tokovi vrijednosti definiraju ŠTO radite.

PROCES
(eng. Process)
Proces: Skup međusobno povezanih ili interaktivnih aktivnosti koje pretvaraju ulaze u izlaze. Proces uzima jedan ili više definiranih ulaza i pretvara ih u definirane izlaze. Procesi definiraju redoslijed postupaka i njihove ovisnosti. Procesi definiraju KAKO radite.
Strukturiranje aktivnosti organizacije u obliku tokova vrijednosti omogućava jasnu sliku onoga što i kako se isporučuje, kao i kontinuirano poboljšavanje usluga.

SUSTAV VRIJEDNOSTI USLUGE
(eng. Service Value System (SVS))
… da bi upravljanje uslugama pravilno funkcioniralo, mora funkcionirati kao sustav.
SUSTAV VRIJEDNOSTI USLUGE
(eng. Service Value System (SVS))
ITIL SVS opisuje kako sve komponente i aktivnosti organizacije djeluju zajedno kao sustav koji omogućava stvaranje vrijednosti.
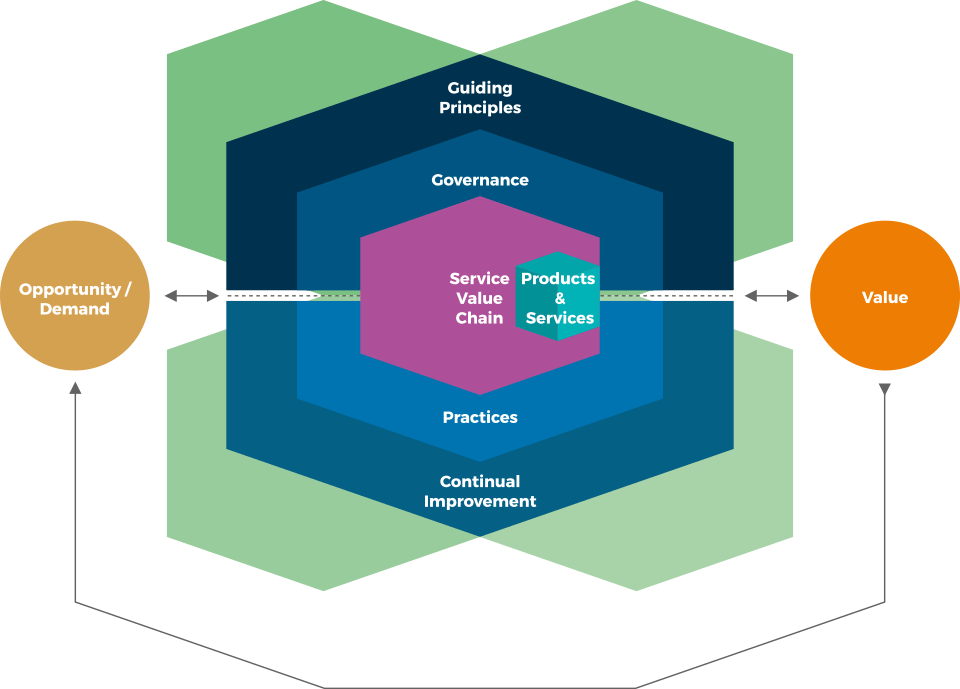

SERVICE VALUE SYSTEM (SVS) – detaljnije
…od PRILIKE/ZAHTJEVA do VRIJEDNOSTI
PRILIKA & POTREBA
(eng. Opportunity & Demand)
PRODUKTI & USLUGE
(eng. Products & Services)
VRIJEDNOST
(eng. Value)
ITIL Sustav vrijednosti usluge (SVS) omogućava organizacijama “putovanje”
od PRILIKE/POTREBA do postizanja organizacijskih ciljeva, pružanja USLUGA i konačno zajedničkog stvaranja VRIJEDNOSTI s dionicima …
… i da bi ovo “putovanje” bilo uspješno, sve SVS komponente moraju djelovati kao sustav! …
SVS KOMPONENTE
VODEĆA NAČELA
(eng. Guiding principles)
UPRAVLJANJE
(eng. Governance)
LANAC VRIJEDNOSTI USLUGE
(eng. Service value chain)
PRAKSE
(eng. Practices)
KONTINUIRANO POBOLJŠANJE
(eng. Continual Improvement)

PRILIKA & POTREBA
(eng. Opportunity & Demand)
Prilika i potražnja pokreću aktivnosti unutar ITIL SVS-a, a te aktivnosti vode stvaranju vrijednosti.
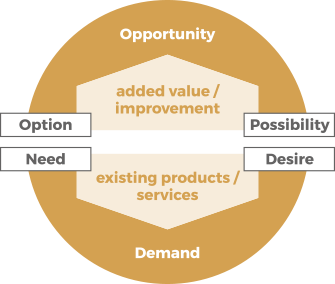

PRILIKA
(eng. Opportunity)
Prilike su mogućnosti za dodavanje vrijednosti za dionike ili poboljšanje same organizacije.

POTREBA
(eng. Demand)
Potreba je potreba/želja za proizvodima i uslugama od strane internih ili eksternih konzumenata.

VODEĆA NAČELA
(eng. Guiding principles)
Vodeća načela su preporuke koje mogu voditi organizaciju u svim okolnostima, bez obzira na promjene u njezinim ciljevima, strategijama, vrstama rada ili upravljačkoj strukturi.
ITIL VODEĆA NAČELA
(eng. Guiding principles)
… usmjeravaju odluke i postupke organizacije i osiguravaju zajedničko razumijevanje i zajednički pristup upravljanju uslugama u cijeloj organizaciji.
![guiding_principles[1]](https://www.itsm.hr/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/wsi-imageoptim-guiding_principles1.png)

7 VODEĆIH NAČELA
(eng. 7 Guiding principles)
(eng. 7 Guiding principles)
VODEĆA NAČELA …
… vode organizacije pri USVAJANJU pristup upravljanju uslugama.
… vode organizacije pri PRILAGODBI ITILa sukladno vlastitim specifičnim potrebama i okolnostima.
… potiču i podržavaju organizacije u kontinuiranom poboljšavanju na svim razinama.
… omogućavaju organizacijama učinkovitu integriraju i uporabu više metoda u sveukupni pristup upravljanju uslugama.

UPRAVLJANJE
(eng. Governance)
Organizacijsko upravljanje je sustav kojim se organizacija usmjerava i kontrolira.
Upravljanje se ostvaruje kroz aktivnosti: Evaluacije, Usmjeravanja, Nadgledanja koje omogućuju organizacijama kontinuirano usklađenje svojeg poslovanje sa strateškim pravcem koji je postavilo upravljačko tijelo.
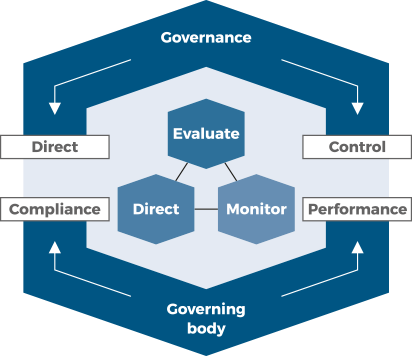

UPRAVLJAČKO TIJELO
(eng. Governing body)
Upravljačko tijelo je osoba ili grupa ljudi koji su na najvišoj razini odgovorni za rad i usklađenost organizacije

LANAC VRIJEDNOSTI USLUGE
(eng. Service Value Chain)
Lanac vrijednosti usluga je operativni model koji opisuje ključne aktivnosti potrebne za odgovor na potražnju i omogućavanje stvaranja vrijednosti kroz stvaranje i upravljanje proizvodima i uslugama.
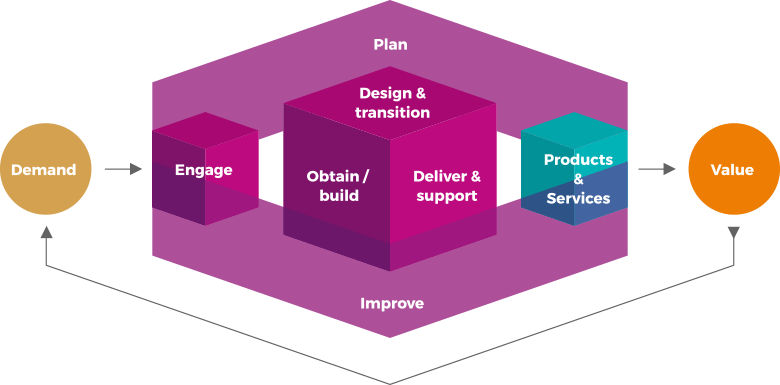
ITIL Lanac vrijednosti usluge uključuje šest aktivnosti lanca vrijednosti.

SERVICE VALUE CHAIN ACTIVITIES
PLANIRNJE (eng. Plan)
osigurava zajedničko razumijevanje vizije, trenutnog stanja i smjera poboljšanja za sve četiri dimenzije i sve proizvode i usluge u cijeloj organizaciji.

POBOLJŠAVANJE (eng. Improve)
osigurava kontinuirano poboljšavanje proizvoda, usluga i praksi u svim aktivnostima lanca vrijednosti i četiri dimenzije upravljanja uslugama.
OBAVEZIVANJE (eng. Engage)
donosi dobro razumijevanje potreba dionika, transparentnost i stalan angažman i dobre odnose sa svim dionicima.

DIZAJN & TRANZICIJA
(eng. Design & Transition)
osigurava da proizvodi i usluge kontinuirano ispunjavaju očekivanja dionika u smislu kvalitete, troškova i vremena isporuke na tržište.
NABAVA/IZRADA
(eng. Obtain/Build)
osigurava da su komponente usluge dostupne kad i gdje su potrebne i da ispunjavaju dogovorene specifikacije.

ISPORUKA & PODRŠKA
(eng. Deliver & Support)
osigurava isporuku i podršku usluga u skladu s dogovorenim specifikacijama i očekivanjima dionika.
Svaka se aktivnost može oslanjati na unutarnje resurse ili treće strane, procese, vještine i kompetencije iz jedne ili više praksi…..

PRAKSE
(eng. Practices)
Skup organizacijskih resursa namijenjenih za obavljanje poslova ili za postizanje nekog cilja. Ti su resursi grupirani u četiri dimenzije upravljanja uslugama.
![practices[1]](https://www.itsm.hr/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/wsi-imageoptim-practices1.png)

GENERALNE PRAKSE UPRAVLJANJA
(eng. General Management Practices)

PRAKSE UPRAVLJANJA USLUGAMA
(eng. Service management practices)

PRAKSE UPRAVLJANJA TEHNOLOGIJOM
(eng. Technical management practices)

KONTINUIRANO POBOLJŠANJE
(eng. Continual Improvement)
Neprekidno poboljšavanje je ponavljajuća organizacijska aktivnost koja se izvodi na svim razinama kako bi se osigurala uspješnost organizacije u kontinuiranom ispunjava očekivanja dionika.

ITIL MODEL KONTINUIRANOG POBOLJŠANAJ
(eng. Continual improvement model)
ITIL Model kontinuiranog poboljšanja pruža organizacijama strukturiran pristup provedbi poboljšanja./p>
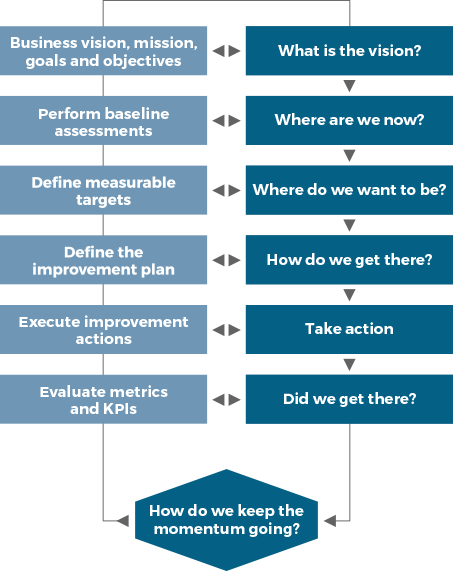
Model kontinuiranog poboljšanja primjenjuje se na SVS u cjelini, kao i na sve proizvode, usluge, komponente usluge i odnose u organizaciji.

PRODUKTI & USLUGE
(eng. Products & Services)

USLUGA ( eng Service)
Usluga je način koje omogućuje stvaranje vrijednosti omogućavajući ishode koje klijenti žele postići, bez da klijent upravlja određenim troškovima i rizicima.

PRODUKT (eng Product)
Konfiguracija resursa organizacije koja je dizajnirana tako da ponudi vrijednost konzumentu.
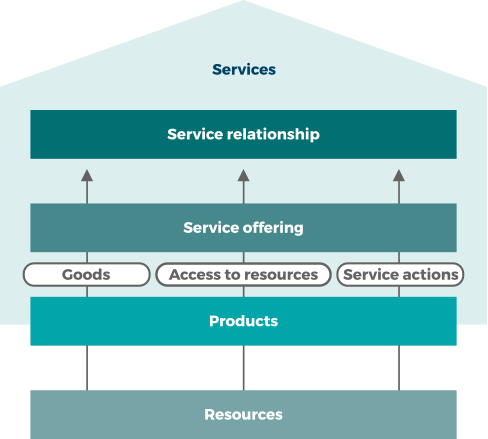

PONUDA USLUGA ( eng. Service Offering)
Opis jedne ili više usluga, osmišljenih da udovolje potrebama ciljne skupine potrošača. Ponuda usluga može uključivati robu, pristup resursima i obavljanje radnji vezano uz uslugu.

USLUŽNI ODNOS (eng. Service relationship)
Suradnja između pružatelja usluga i konzumenta usluga. Uslužni odnosi uključuju pružanje usluga, potrošnju usluge i upravljanje uslužnim odnosom.

VRIJEDNOST ( eng. Value)
Vrijednost su percipirane koristi, korisnost i važnost nečega.
Uslužni odnosi se smatraju vrijednim samo ako imaju više pozitivnih učinaka nego negativnih.

NEGATIVNI EFEKTI
Uslužni odnosi mogu uvesti nove rizike i troškove, a u nekim slučajevima mogu negativno utjecati na neke planirane ishode, istovremeno podržavajući druge.

POZITIVNI EFEKTI
Pružatelji usluga pomažu svojim klijentima u postizanju ishoda i pri tome preuzimaju neke povezane rizike i troškove.
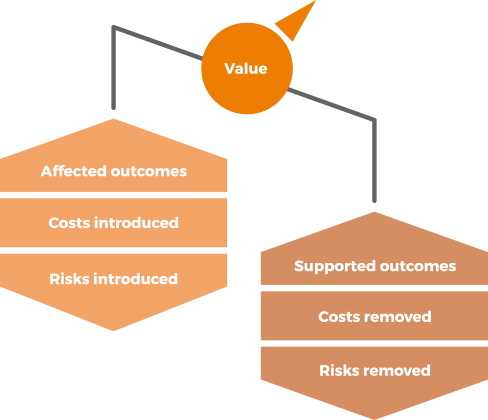
ISHODI, TROŠKOVI & RIZICI
(eng. Outcome, Cost & Risk)

ISHOD
( eng. Outcome)
Ishod je rezultat za dionika omogućen jednom ili više isporuka (eng. output).

TROŠAK
(eng. Cost)
Trošak je iznos novca koji se potroši na određenu aktivnost ili resurs.

RIZIK
(eng. Risk)
Rizik je mogući događaj koji bi mogao nanijeti štetu ili gubitak ili otežati postizanje ciljeva.
… ili neizvjesnost ishoda.

KORISNOST & JAMSTVO
(eng. Utility & Warranty)
Iz perspektive klijenta, vrijednost se sastoji od dva osnovna elementa: korisnost (prikladnost za svrhu) i jamstvo (prikladnost za upotrebu).

KORISNOST
(eng. Utility)
‘what the service does’
Funkcionalnost koju nudi proizvod ili usluga za zadovoljavanje određene potrebe. Korisnost se može sažeti kao “što usluga radi” i određuje je li usluga “prikladna za svrhu”. Da bi imala korisnost, usluga mora podržavati potrošačeve performanse ili uklanjati ograničenja od potrošača. Mnoge usluge rade i jedno i drugo.

JAMSTVO
(eng. Warranty)
‘KAKO je usluga performansno’
Uvjerenje da će proizvod ili usluga ispuniti dogovorene zahtjeve. Jamstvo se može sažeti kao “način na koji usluga funkcionira” i pomoću kojeg se može utvrditi je li usluga “prikladna za upotrebu”. Jamstvo se često odnosi na razine usluge usklađene s potrebama potrošača usluga.

